Structure and Components
- Tube Body: Made of medical-grade glass or plastic (e.g., PET), typically cylindrical with a sealed bottom and an open top covered by a rubber stopper.
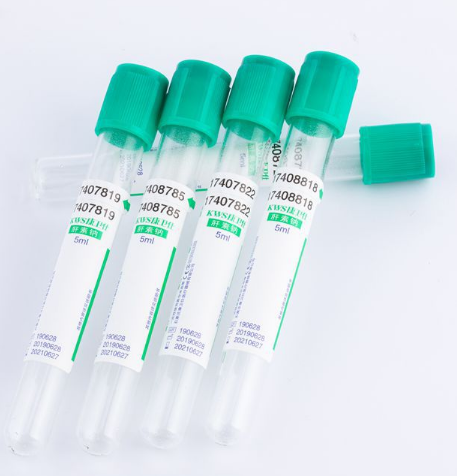
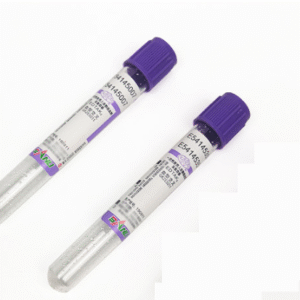
- Stopper: Color-coded to indicate different additives or purposes (e.g., red, purple, blue, green), ensuring quick identification. The stopper is airtight to maintain sample integrity.
- Vacuum System: Pre-vacuumed to draw a specific volume of blood (e.g., 5 mL, 10 mL) when the needle is inserted, eliminating the need for manual suction.
Key Features and Functions
- Additives (Depending on Type):
- Anticoagulants:
- Heparin (green stopper): Prevents clotting by inhibiting thrombin, suitable for plasma-based tests (e.g., chemistry panels).
- EDTA (purple stopper): Chelates calcium ions, used for hematology tests (e.g., complete blood count, CBC).
- Sodium citrate (blue stopper): Binds calcium, essential for coagulation studies (e.g., PT, aPTT).
- Clot Activators:
- Silica particles or glass beads (red/yellow stopper): Accelerate clotting for serum separation (e.g., blood chemistry, immunoassays).
- Gel Separators:
- Thixotropic gel (often in red or gold stoppers): Settles between serum/plasma and cells during centrifugation, maintaining sample layers.
- Anticoagulants:
- Labeling: Pre-printed with patient information fields (name, ID, date), barcode for tracking, and additive type.
Usage Scenarios
- Clinical Diagnostics: Blood tests for routine check-ups, disease monitoring, or emergency medicine.
- Research Labs: Sample collection for biomedical studies, clinical trials, or genetic analysis.
- Blood Banks: Temporary storage of blood donations before processing.
Standards and Safety
- Complies with international standards (e.g., ISO 15189 for medical laboratories).
- Designed to minimize hemolysis (red blood cell rupture) and contamination, with sterile packaging for single-use.